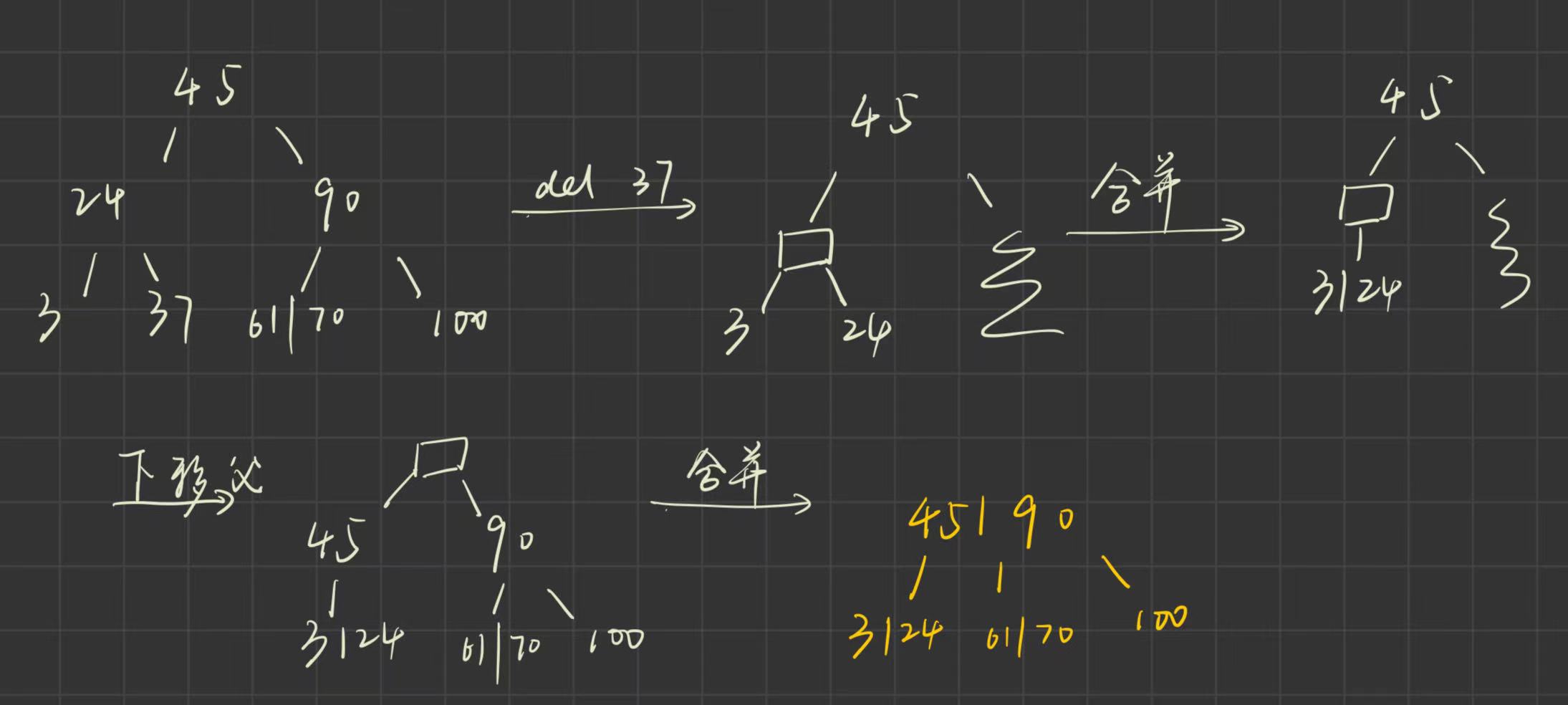链表栈队
链表操作
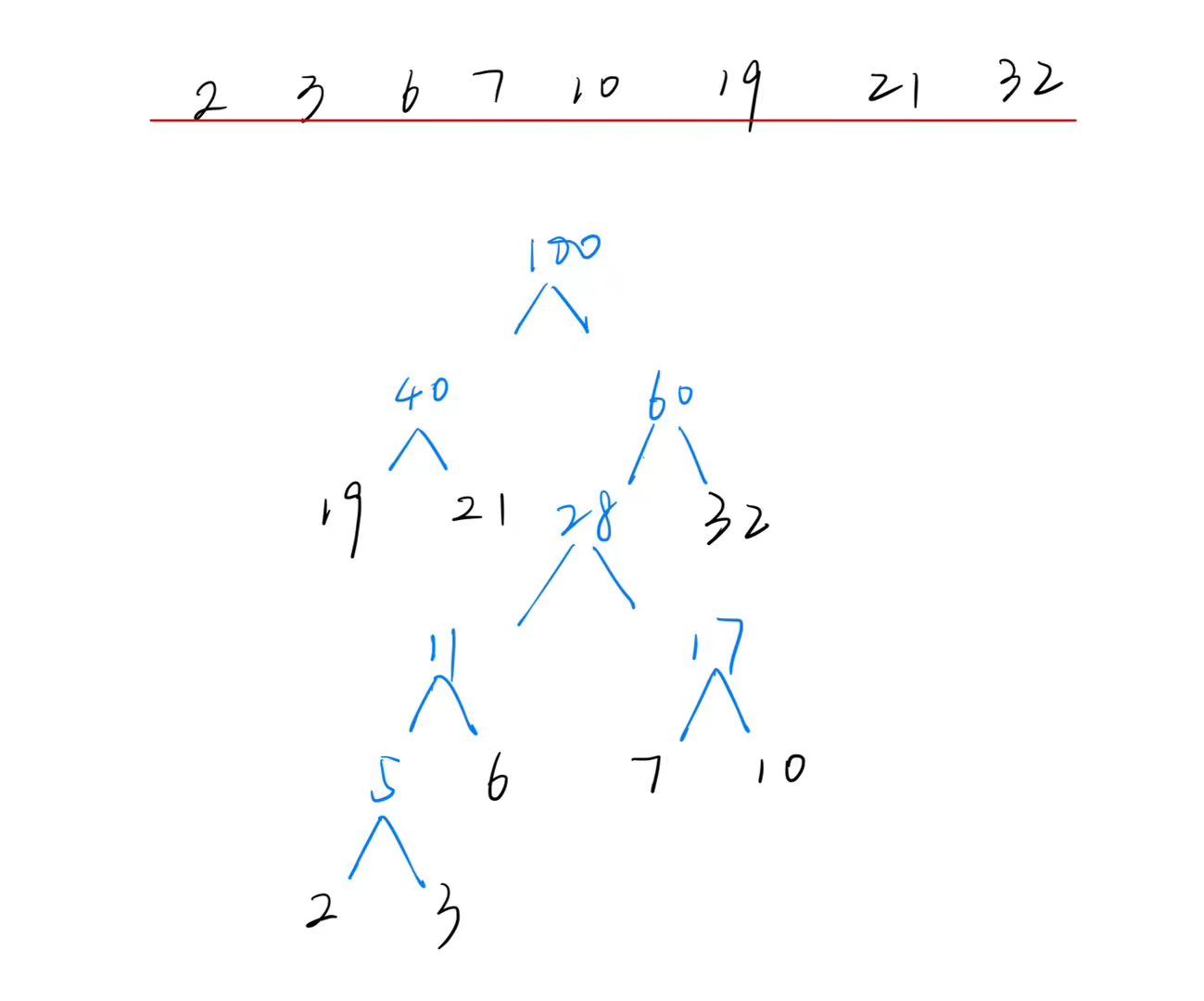
有序链表的合并
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
{
Node*newnode=new Node;
newnode->next=NULL;
newnode->data=data;
Node*cur=list;
while(cur->next!=NULL)
{
cur=cur->next;
}
cur->next=newnode;
return;
}
List MergeList(List &listA,List &listB)
{
List listC;
InitList(listC); // 初始化合并后的链表
Node*curA=listA->next;
Node*curB=listB->next;
while(curA!=NULL&&curB!=NULL)
{
if(curA->data>=curB->data)
{
AddNode(listC,curB->data);
curB=curB->next;
}
else if(curA->data<curB->data)
{
AddNode(listC,curA->data);
curA=curA->next;
}
}
while(curA!=NULL)
{
AddNode(listC,curA->data);
curA=curA->next;
}
while(curB!=NULL)
{
AddNode(listC,curB->data);
curB=curB->next;
}
return listC;
}查找链表倒数第k个数据(快慢指针)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
Node* FindMthNode(const List& list, int m){
Node* p1 = list;
Node* p2 = list;
// 让p2指针向后移动m-1步
for(int i = 0; i < m-1; i++){
if(p2 == NULL) return NULL; // 如果链表长度小于m,返回NULL
p2 = p2->next;
}
// 同时移动p1和p2指针,直到p2指向链表的最后一个节点
while(p2->next != NULL){
p1 = p1->next;
p2 = p2->next;
}
return p1;
}链表的反转
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
int InitList(List &list){
list=new Node;
list->next=NULL;
return 0;
}
int DestroyList(List &list){
Node* cur = list;
while (cur != NULL) {
Node* temp = cur;
cur = cur->next;
delete temp;
}
list = NULL;
return 0;
}
int AddNode(List &list, int data){
Node*newnode=new Node;
newnode->next=NULL;
newnode->data=data;
Node*cur=list;
while(cur->next!=NULL)
{
cur=cur->next;
}
cur->next=newnode;
return 0;
}
>/*链表反转*/
void ReverseList(List &list){
Node*cur=list->next;
Node*prev=NULL;
while(cur!=NULL)
{
Node*next=cur->next;
cur->next=prev;
prev=cur;
cur=next;
}
list->next=prev;
}
括号匹配
最最最基础的括号匹配
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
using namespace std;
struct Node{
char data;
Node* next;
};
typedef Node* Stack;
void InitStack(Stack& S) {
// TODO: Initialize the stack.
S=new Node;
S->next=NULL;
return;
}
void DestroyStack(Stack& S) {
// TODO: Destroy the stack and free all nodes.
Node*cur=S;
while(cur!=NULL)
{
Node*tmp=cur;
cur=cur->next;
delete tmp;
}
S=NULL;
return ;
}
void Push(Stack& S, char data) {
// TODO: Push an element onto the stack.
Node*newnode= new Node;
newnode->data=data;
newnode->next=S->next;
S->next=newnode;
return;
}
bool IsEmpty(const Stack& S) {
return S == nullptr; // This check is preserved as it's non-functional.
}
char Pop(Stack& S) {
if (IsEmpty(S)) {
return '\0'; // Return null character if stack is empty.
}
// TODO: Pop an element from the stack.
else{
Node*tmp=S->next;
S->next=tmp->next;
delete tmp;
}
return '\0'; // Return the popped element or null character.
>}
bool isMatching(const string& str) {
Stack S;
InitStack(S);
for (char c : str) {
// TODO: Process each character based on the given conditions.
if(c=='(')
Push(S,c);
else{
if(S->next!=NULL){
Pop(S);
}
else{
return false;//条件一:输入)时占栈不为空
}
}
}
bool result = IsEmpty(S->next); // 条件二:字符串输入完成后后栈为空
DestroyStack(S);
return result;
}
void BracketMatch() {
string line;
while (getline(cin, line))
{
if(isMatching(line))
{
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
}
else{
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
}
}
}
int main() {
BracketMatch();
return 0;
}
约瑟夫问题
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
using namespace std;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
queue<int> q;
int n,m;
int num[10000];
while(cin>>n>>m)
{
cout<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
num[i]=i+1;
q.push(num[i]);
}
while(!q.empty())
{
for(int i =0;i<m;i++){
int x=q.front();
if(i==m-1){
q.pop();
cout<<x<<" ";
}
else{
q.pop();
q.push(x);
}
}
}
}
}
运算表达式
中缀表达式:建立两个栈
后缀表达式:建立一个栈
遇到数字放入栈中,如果遇到操作符则出栈两个数。
中缀转后缀:假设括号,将操作符移动到括号右侧。
杨辉三角
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
{
int n, i, x, temp;
queue<int> Q;
Q.push(1);
for (n = 2; n <= N; n++)
{
Q.push(1);
for (i = 1; i <= n - 2; i++)
{
temp = Q.front();
Q.pop();
cout << temp << " ";
x = Q.front();
temp = temp + x;
Q.push(temp);
}
x = Q.front();
Q.pop();
cout << x << " ";
Q.push(1);
cout << endl;
}
while (!Q.empty())
{
x = Q.front();
Q.pop();
cout << x << " ";
}
}
int main()
{
int N;
cout << "please input the N:";
cin >> N;
YangHuiTriangle(N);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
KMP
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
using namespace std;
void GetNext(char str[],int next[])
{
next[0]=-1;
next[1]=0;//确定next数组中的前两位。
int n=strlen(str);
int x,y;//x用来标记坐标,y用来遍历
for(int y=1;y<n;y++){
x=next[y];
while(str[x]!=str[y]&&x!=-1)//往前面找,如果没有匹配位置则回到x=-1但也不能太往前
{
x=next[x];
}
next[y+1]=x+1;
}
//不断去循环佐证x的位置,最后把值献给y+1
}
void GetNextVal(char str[],int next[],int nextval[])
{
int i=0;
nextval[0]=-1;
int n=strlen(str);
for(i=1;i<n;i++){
int j=next[i];
while(str[i]==str[j]&&j!=-1){
j=next[j];
}
nextval[i]=j;
}
}
int main()
{
char str[1000];
int next[1000];
int nextval[1000];
while(cin>>str) {
int n=strlen(str);
GetNext(str,next);
GetNextVal(str,next,nextva l);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cout<<next[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cout<<nextval[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
稀疏矩阵
三元组法快速转置矩阵
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
using namespace std;
struct TriNode
{
int row, col;
int data;
};
struct TriTable
{
TriNode *datas;
int mu, nu, tu; // 行数,列数,非零元个数
};
int CreateTriTable(TriTable &T, int matrix[], int m, int n)
{
T.mu = m;
T.nu = n;
// 统计非零元的个数,分配存储空间
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m*n; i++)
if (matrix[i] != 0) count++;
T.tu = count;
T.datas = new TriNode[count];
// 填写三元组表
int k = 0, t = 0;
for (int i = 0; i<m; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (matrix[k] != 0)
{
T.datas[t].row = i;
T.datas[t].col = j;
T.datas[t].data = matrix[k];
t++;
}
k++;
}
return 0;
}
int DestroyTriTable(TriTable &T)
{
delete[]T.datas;
T.mu = T.nu = T.tu = 0;
return 0;
}
int PrintTriTable(TriTable &T)
{
cout << "mu = " << T.mu << ", nu = " << T.nu << ", tu = " << T.tu << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < T.tu; i++)
cout << "(" << T.datas[i].row << ", " << T.datas[i].col << ") = "
<< T.datas[i].data << endl;
return 0;
}
/*将三元组表结构的矩阵A转置到B*/
int FastTranspose(TriTable &B, TriTable &A)
{
// 初始化结果三元组表
B.mu = A.nu;
B.nu = A.mu;
B.tu = A.tu;
B.datas = new TriNode[B.tu];
// 统计结果矩阵每行非零元个数
int *rsum = new int[B.mu];
for (int i = 0; i < B.mu; i++) rsum[i] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < A.tu; i++)
rsum[A.datas[i].col]++;
/*新开数组的大小与转置矩阵的行数相同*/
/*位置数组的大小与三元组的数量有关*/
// 计算结果矩阵各行在三元组表中的起始下标
int *rpos = new int[B.mu];
rpos[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < B.mu; i++)
rpos[i] = rpos[i - 1] + rsum[i - 1];
// 将源三元组表转置到目标三元组表中
for (int i = 0; i < A.tu; i++)
{
int j = rpos[A.datas[i].col];
B.datas[j].row = A.datas[i].col;
B.datas[j].col = A.datas[i].row;
B.datas[j].data = A.datas[i].data;
rpos[A.datas[i].col]++;
}
delete[]rpos;
delete[]rsum;
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int *matrix, m, n;
cout << "请输入行数 列数:";
cin >> m >> n;
matrix = new int[m*n];
cout << "请按行优先顺序输入矩阵:";
for (int i = 0; i < m*n; i++)
cin >> matrix[i];
TriTable T1;
CreateTriTable(T1, matrix, m, n);
cout << "源矩阵:" << endl;
PrintTriTable(T1);
TriTable T2;
FastTranspose(T2, T1);
cout << "转置后矩阵:" << endl;
PrintTriTable(T2);
DestroyTriTable(T1);
DestroyTriTable(T2);
delete []matrix;
return 0;
}
高维下标转换
树
树的概念与结论
分类
满二叉树:
每一层的节点都达到了最大值,如果有k层。那么最多有2**k-1个节点。
完全二叉树
前k-1层是满的,最后一层从左到右是连续的。高度为h的完全二叉树节点范围是【2^(h-1), 2^h-1】,最后一层最少一个。
小结论
- 任意一个二叉树,如果度为0的节点有n0个,度为2的节点有n2个。那么n0=n2+1。
- 完全二叉树,n1要么为0要么为1。
- 不存在度大于二的节点
物理存储的下标关系:
parent=(child-1)/2两个孩子算出来的整数部分都是相同的
leftchild=parent*2+1
rightchild=parent*2+2
树的基础操作
树的初始化
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
using namespace std;
typedef struct Node
{
char data;
Node*lchild;
Node*rchild;
}Node,*BiTree;
/*初始化树*/
void InitTree(BiTree&tree)
{
tree=NULL;
}树的前序输入
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
char* GetTree(BiTree&tree,char*str)
{
//如果带存入的数据为空,则将该节点置空,数组下标移到下一个
if('#'==*str)
{
tree=NULL;
return str+1;
}
//如果存入数据不为空,新建结点存入数据
tree=new Node;
tree->data=*str;
char*afterleft=GetTree(tree->lchild,str+1);//顺着左侧结点继续输入
char*afterright=GetTree(tree->rchild,afterleft);
return afterright;
}销毁一棵树
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
void DestroyBiTree(BiTree& tree)
{
if (tree != NULL) {
DestroyBiTree(tree->lchild); // 递归删除左子树
DestroyBiTree(tree->rchild); // 递归删除右子树
delete tree; // 删除当前节点
tree = NULL;
}
}
树的四种遍历
递归版本
前序遍历
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
{
//先引入头结点
queue<Tree>q;
Tree p=tree;
q.push(p);
//判断队列是否为空
while(!q.empty())
{
Tree tmp=q.front();
q.pop();
cout<<tmp->data<<"";
//入队两个新节点
if(tmp->leftchild)q.push(tmp->leftchild);
if(tmp->rightchild)q.push(tmp->rightchild);
}
}中序遍历
略略略~
后续遍历
略略略~
非递归版本
前序遍历
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
void Pretraverse(Tree&tree)
{
stack<Tree>s;
Tree p=tree;
while(!s.empty()||p!=NULL)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<"";
s.push(p);
p=p->leftchild;
}
if(!s.empty())
{
Tree tmp=s.top();
s.pop();
p=tmp->rightchild;
}
}
}中序遍历
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
void Intraverse(Tree&tree)
{
stack<Tree>s;
Tree p=tree;
while(!s.empty()||p!=NULL)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
s.push(p);
p=p->leftchild;
}
if(!s.empty())
{
Tree tmp=s.top();
s.pop();
p=tmp->rightchild;
cout<<tmp->data<<"";
}
}
}后续遍历
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
void Suctraverse(Tree&tree)
{
stack<Tree>s,t;
Tree p=tree;
while(!s.empty()||p!=NULL)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
t.push(p);
s.push(p);
p=p->rightchild;
}
if(!s.empty())
{
Tree tmp=s.top();
s.pop();
p=tmp->leftchild;
}
}
while(!t.empty())
{
Tree tmp=t.top();
t.pop();
cout<<tmp->data<<"";
}
}层序遍历
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
void LevelTravel(Node* tree)
{
if(tree == nullptr) {
return;
}
queue<Node*> Q;
Q.push(tree);
while(!Q.empty())
{
Node* q = Q.front();
cout << q->data << " ";
Q.pop();
if (q->lchild) {
Q.push(q->lchild);
}
if (q->rchild) {
Q.push(q->rchild);
}
}
}
树的计算
树整体结点个数的计算
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
int GetNum(BiTree&tree)
{
if(tree==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int lheight=GetNum(tree->lchild);
int rheight=GetNum(tree->rchild);
return lheight+rheight+1;
}树整体深度的计算
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
int GetHeight(BiTree&tree)
{
if(tree==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int lheight=GetHeight(tree->lchild);
int rheight=GetHeight(tree->rchild);
return max(lheight,rheight)+1;
}计算树的宽度
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
{
if (tree == NULL) {
return 0;
}
int maxWidth = 1; // 记录当前最大宽度
queue<Tree> q;
q.push(tree);
while (!q.empty()) {
int levelSize = q.size(); // 当前层的节点个数
for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
Tree node = q.front();
q.pop();
if (node->leftchild != NULL) {
q.push(node->leftchild);
}
if (node->rightchild != NULL) {
q.push(node->rightchild);
}
}
if (q.size() > maxWidth) {
maxWidth = q.size();
}
}
return maxWidth;
}
树的高级玩法
判断一棵树是否为完全二叉树
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
bool isCompleteBinaryTree(BiTree&tree) {
if (!tree) {
return true;
}
std::queue<Node*> q;
q.push(tree);
while (!q.empty())
{
Node* current = q.front();
q.pop();
if (!current) //如果层序遍历过程中出现了空
{
while (!q.empty()) //需要检验后续遍历所有的结点是否都为空,否则就return false
{
Node* temp = q.front();
q.pop();
if (temp)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
q.push(current->lchild);
q.push(current->rchild);
}
return true;
}根据前序与中序遍历还原二叉树
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
BiTree PreInTree(const char *pre,const char *mid,int x)
{
if(x<=0) return NULL;//如果root==-1,无论左子树还是右子树都不会继续递归
BiTree t=new Node;
t->data=*pre;
int root=-1;
for(int i=0;i<x;i++){
if(mid[i]==*pre){
root=i;//找到中序遍历中“中点”的位置
break;
}
}
t->lchild=PreInTree(pre+1,mid,root);//在中序的左半边找左孩子
t->rchild=PreInTree(pre+1+root,mid+1+root,x-root-1);//在中序的右半边找右孩子,初始下标为mid+1+root,查找范围是这个下标后的x-root-1个数据
return t;
}
网格法前序中序还原二叉树
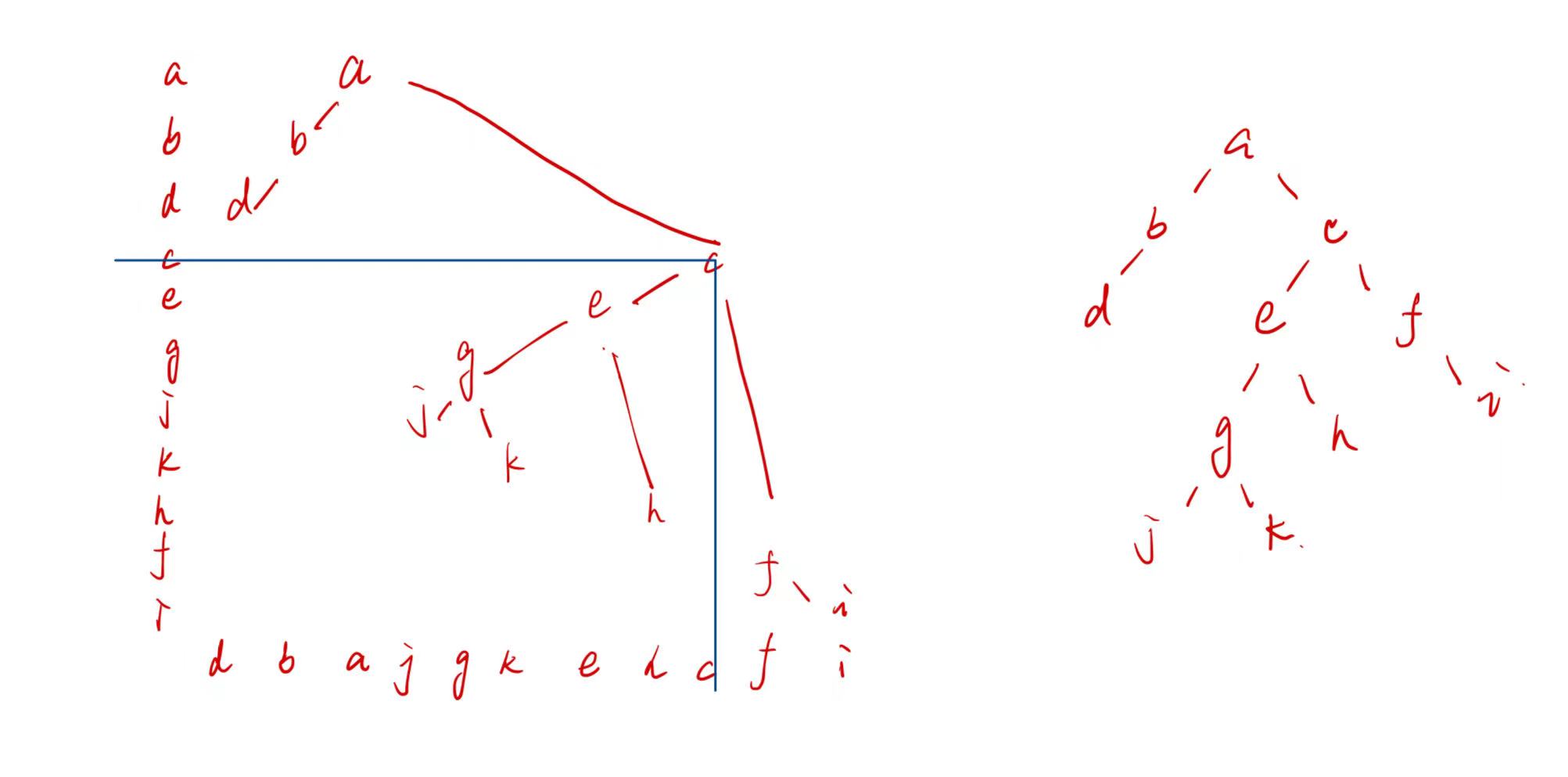
x轴写中序,y轴写前序遍历。
N叉树转化为二叉树
兄弟结点之间连线,去除父亲结点与长子之外的连线。
森林转化为二叉树
将所有N叉树转化为二叉树,再将二叉树之间以父亲结点与右孩子的方式连接
二叉树转化为树
父亲结点与左孩子的右孩子连线,去除左孩子与右孩子的连线。
二叉树转化为森林
断开所有父节点与右孩子的连线,再由二叉树转化为树
哈夫曼树的理解
图
邻接矩阵遍历
MartrixDFS
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
void DFS(const Graph& G, int v0, int visited[]){
// 第一步: 先访问v0,标记已访问
visited[v0]=1;
cout<<v0<<" ";
// 第二步: 再对v0的所有未被访问的邻接点进行DFS
for(int j=0;j<G.vexNumber;j++)
{
if(G.adjMatrix[v0][j]&&!visited[j])
{
DFS(G,j,visited);
}
}
}
// 对整个图进行DFS
void DFS(const Graph& G){
// 第一步:初始化visited数组
int visited[1000];
for(int i =0;i<G.vexNumber;i++){
visited[i]=0;
}
// 第二步:以每个未被遍历的顶点为起点,进行DFS
for(int i =0;i<G.vexNumber;i++){
if(visited[i]==1)
{
continue;
}
else{
DFS(G,i,visited);
}
}
}MartrixBFS
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
void BFS(const Graph& G){
// 第一步:初始化visited数组
int visited[1000];
for(int i =0;i<G.vexNumber;i++){
visited[i]=0;
}
// 第二步: 挨个挑结点作为起点遍历整个图
for(int i =0;i<G.vexNumber;i++){
if(visited[i]==1)
{
continue;
}
visited[i]=1;
cout<<i<<" ";
q.push(i);
while(!q.empty())
{
int x=q.front();
q.pop();
//按选定结点继续BFS发散
for(int j=0;j<G.vexNumber;j++)
{
if(G.adjMatrix[x][j]&&!visited[j])
{
visited[j]=1;
cout<<j<<" ";
q.push(j);
}
}
}
}
}
连通分量问题
Finished序列
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
visited[v0]=1;
for(int j=0;j<G.vexNumber;j++)
{
if(G.adjMatrix[v0][j]&&!visited[j])
{
DFS(G,j,visited);
}
}
cout<<v0<<" ";//每次遍历结果都与深度遍历反向输出
}
// 对整个图进行DFS
void FinishDFS(const Graph& G){
int visited[1000];
for(int i =0;i<G.vexNumber;i++){
visited[i]=0;
}
for(int i =0;i<G.vexNumber;i++){
if(visited[i]==1)
{
continue;
}
else{
DFS(G,i,visited);
}
}
}
拓扑排序
判断是否是有效拓扑序列:
计算每个结点的入度,按照入度为0的结点开始检测,删除结点出度。
最早发生时间:
每个结点在全部前面限制要素都被满足后,最早开始的时间(加上前面结点的最大值,使之自身最大)
最迟发生时间:
从终点开始倒推,计算前面结点的的最迟发生时间,否则就会影响最终结果(减去后面结点的最大值,使得自身最小)
最早工期问题:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
{
stack<int> s;
int max=0;
for(int i=0;i<g.nodeNumber;i++)
{
if(max<g.ve[i]) max=g.ve[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<g.nodeNumber;i++){
g.vl[i]=max;
if(outDegree[i]==0)
s.push(i);
}
while(!s.empty()){
int q=s.top();
s.pop();
for(int i=0;i<g.nodeNumber;i++)
{
if(g.adjMatrix[i][q]==1)
{
outDegree[i]--;
if(g.vl[i]>g.vl[q]-g.weight[i][q])
g.vl[i]=g.vl[q]-g.weight[i][q];
if(outDegree[i]==0) s.push(i);
}
}
}
}最终取所有结点的最早发生时间就是最短工期。
最小生成树
最小生成树
生成树的概念:一个有 n 个结点的连通图的生成树是原图的极小连通子图,且包含原图中的所有 n 个结点,并且有保持图连通的最少的边。(再加一条边就会出现回路)
最小生成树:边的权重之和最小
MST性质
设无向图G=(V, E),U 是顶点集V的一个非空子集。若(u , v )是一条具有最小权值(代价)的边,其中u∈U, v∈V - U,则必存在一棵包含边(u,v)的最小生成树
Prim算法:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
{
int num=graph.NumVertex;
int cost[200];
int adj[200];//已经纳入路径的结点到达其余结点的距离
int totalcost=0;
cost[0]=-1;
adj[0]=0;
//初始化cost数组
for(int i=1;i<num;i++)
{
cost[i]=graph.edge[0][i];
adj[i]=0;
}
//每次取一个顶点
for(int i=1;i<num;i++)
{
int k=0;
int minicost=999;
//【找最小】:找到目前所有连接点中最小的那个
for(int j=1;j<num;j++)
{
if(cost[j]>0&&cost[j]<minicost)
{
minicost=cost[j];
k=j;
}
}
//成功加入最小的那个
cout<<"minicost"<<i<<": "<<minicost<<endl;
totalcost+=minicost;
cost[k]=-1;
//【做替换】:在新加入的范围内去更新所有点的连接,看看有没有多出来更短的路线
for(int j=1;j<num;j++)
{
if(graph.edge[k][j]<cost[j]&&graph.edge[k][j]!=0&&cost[j]>0)//之前可达的结点有更优路径
{
cost[j]=graph.edge[k][j];
adj[j]=k;
}
if(graph.edge[k][j]!=0&&cost[j]==0)//之前不可达,加入了新节点可达
{
cost[j]=graph.edge[k][j];
adj[j]=k;
}
}
}
cout<<"最小总权重";
cout<<totalcost<<endl;
}
/*测试用例,数组中的元素存在三种状态,第一种是已经cost=-1:表示该点已经在U之内,第二种是cost=0;表示该点不可达;第三种是cost>0,表示可达,有路径需要比较
0 10 9 13 0 0 0
10 0 0 15 7 0 12
9 0 0 4 0 3 0
13 15 4 0 0 22 23
0 7 0 0 0 0 20
0 0 3 22 0 0 32
0 12 0 23 20 32 0
*/Kruskal算法
E1:将所有的边按权值排序;
E2:设每个顶点为一个独立的点集,生成树T为空集;
E3:依序扫描每一条边<vi,vj>,直到已输出n-1条边:
- E31:若vi、vj不在同一点集中,则将该边加入生成树T中,并合并这两个点集;否则舍弃该边;
最短路径
DijKstra
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
using namespace std;
typedef struct{
int NumVertex;
string vertex;
int edge[MAX][MAX];
}GraphMatrix;
void Dijkstra(GraphMatrix&graph,int start)
{
int finish[MAX];
int shortest[MAX];
//初始化
for(int i=0;i<graph.NumVertex;i++){
finish[i]=0;
if(graph.edge[start][i]!=0)
shortest[i]=graph.edge[start][i];
else{
shortest[i]=INF;
}
}
//第一个结点
finish[start]=1;
for(int i=0;i<graph.NumVertex-1;i++){
int min=100000;
//找结点
int k=-1;
for(int j=0;j<graph.NumVertex;j++)
{
if(!finish[j]&&shortest[j]<min)
{
min=shortest[j];
k=j;
}
}
finish[k]=1;
//更新shortest
for(int j=0;j<graph.NumVertex;j++)
{
if(shortest[j]>shortest[k]+graph.edge[k][j]&&graph.edge[k][j]!=0)
{
shortest[j]=shortest[k]+graph.edge[k][j];
}
}
}
//输出到每个节点的最短路径
for(int i=0;i<graph.NumVertex;i++){
if(i!=start)
{
if(shortest[i]==INF)
cout<<"-1"<<" ";//不可达
else{
cout<<shortest[i]<<" ";
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
GraphMatrix graph;
int start;
cin>>graph.NumVertex>>start;
InputMatrixGraph(graph);
Dijkstra(graph,start);
return 0;
}
/*
0 10 9 13 0 0 0
10 0 0 15 7 0 12
9 0 0 4 0 3 0
13 15 4 0 0 22 23
0 7 0 0 0 0 20
0 0 3 22 0 0 32
0 12 0 23 20 32 0
*/
/*
4 1
0 3 0 1
0 0 4 0
2 0 0 0
0 0 1 0
6 4 7
*/FLOYD
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
using namespace std;
typedef struct{
int NumVertex;
string vertex;
int edge[MAXSIZE][MAXSIZE];
}GraphMatrix;
void Floyd(GraphMatrix&graph,int start)
{
int num=graph.NumVertex;
int path[200][200];//记录到该结点的结点
int shortest[200][200];//记录到该点的最短路径;
for(int i=0;i<num;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<num;j++)
{
if(graph.edge[i][j]==0)
{
path[i][j]=INF;
shortest[i][j]=INF;
}
else{
shortest[i][j]=graph.edge[i][j];
path[i][j]=graph.edge[i][j];
}
}
}
for(int k=0;k<num;k++)
{
for(int i=0;i<num;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<num;j++)
{
if(shortest[i][k]==INF||shortest[k][j]==INF)//不可达,故跳过
{
continue;
}
if(shortest[i][k]+shortest[k][j]<shortest[i][j])
{
shortest[i][j]=shortest[i][k]+shortest[k][j];
path[i][j]=k;
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
GraphMatrix graph;
InputMatrixGraph(graph);
Floyd(graph,0);
return 0;
}
/*
4
0 3 0 1
0 0 4 0
2 0 0 0
0 0 1 0
输出
0 3 2 1
6 0 4 7
2 5 0 3
3 6 1 0
*/
查找
概念
平均查找长度(Average Search Length)
ASL是衡量一个查找算法的重要性能指标。
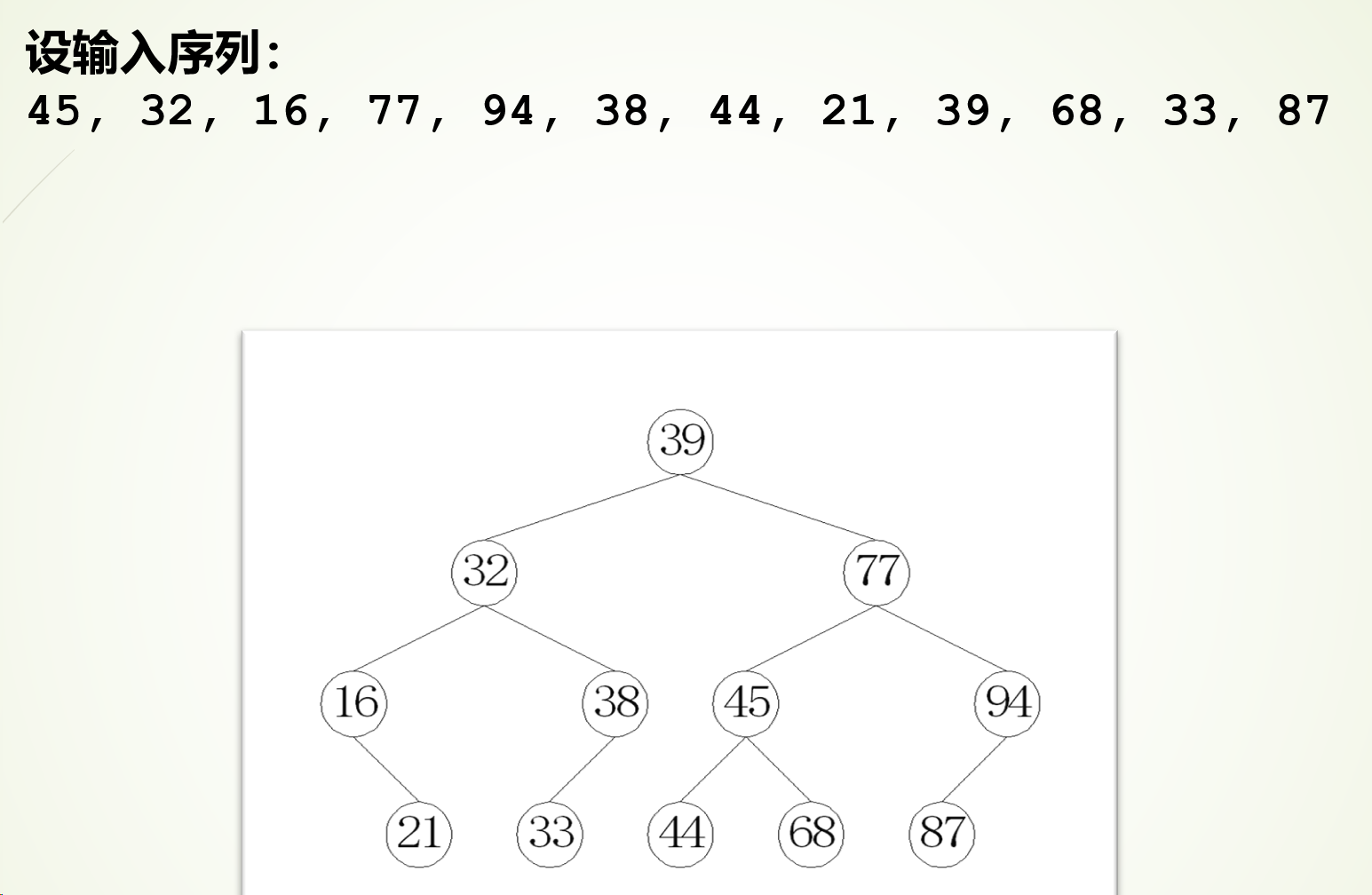
排序二叉树
ASL = logN
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
void Insert(BiTree&tree,int x)
{
if(tree==NULL)
{
tree=new BiNode;
tree->data=x;
tree->lchild=NULL;
tree->rchild=NULL;
}
else if(x<tree->data)
{
Insert(tree->lchild,x);
}
else if(x>tree->data)
{
Insert(tree->rchild,x);
}
}
void GetTree(BiTree&tree)
{
int num;
cin>>num;
for(int i=0;i<num;i++)
{
int x;
cin>>x;
Insert(tree,x);
}
}排序二叉树的平衡因子计算:
int BF=Height(*tree*->lchild)-Height(*tree*->rchild);
平衡二叉树
二叉排序树按照中序遍历是递增的。
结点插入以不平衡二叉树的根节点开始,沿着新加入节点的方向,找与之相邻的三个结点
结点删除
①删除叶子结点:直接删去。
②删除结点仅含有左孩子或右孩子:用唯一的一个孩子替换删除的结点。
③删除结点同时包含左孩子右孩子:找到它的后继(中序遍历)将其替换。需要注意中序遍历别找错了。
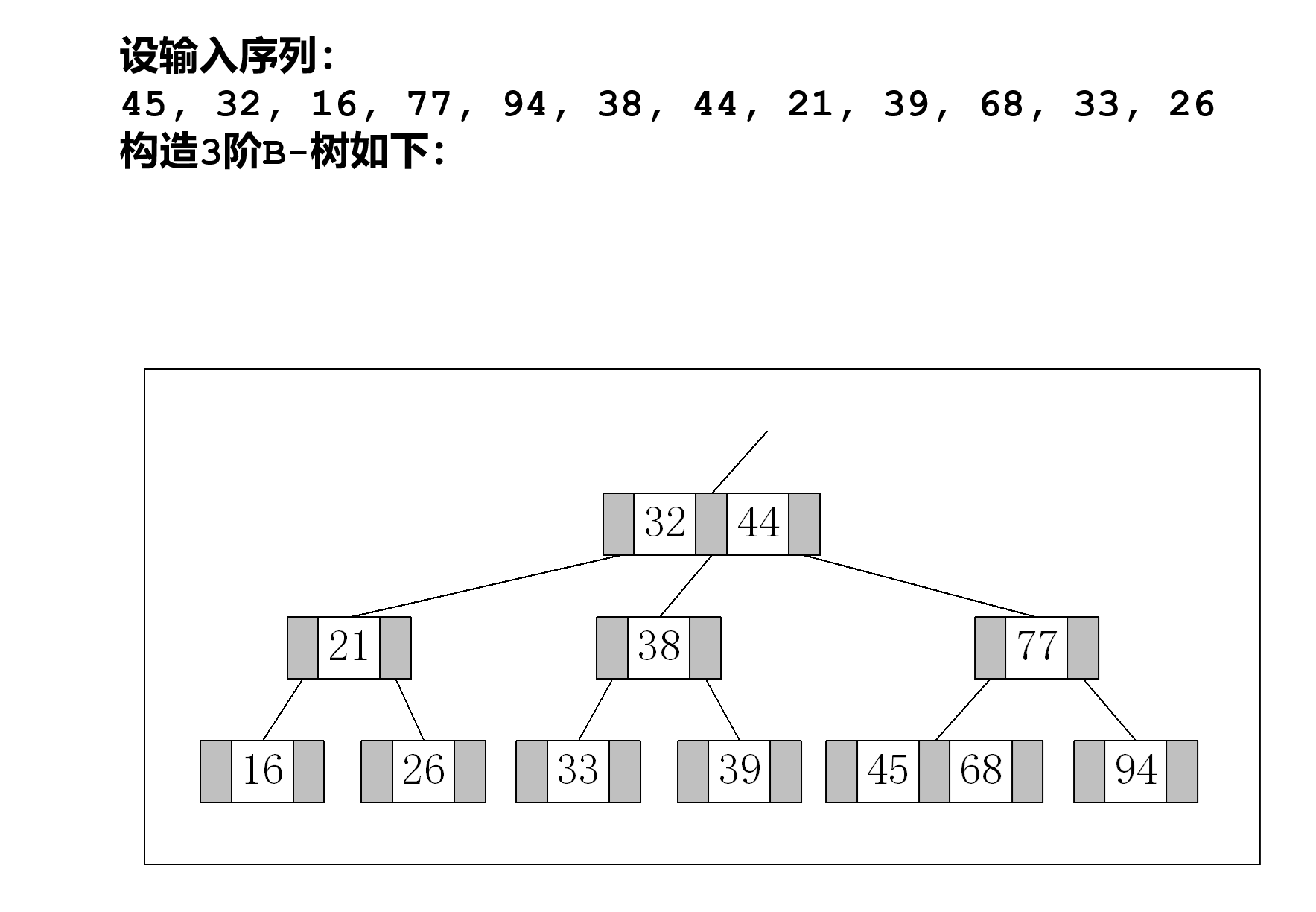
B-树
性质:
N阶-B树每个结点的数据量不超过
N-1,非根结点至少有
N/2(向下取整)个关键字。每个结点最多有
N个分支。分裂插入:
合并删除:
理解:父节点对其子结点负责
删除操作分为三种情况
- 删除叶子结点数据,在叶子结点删除后依然维持>1=个关键字时候,直接删除。否则,需要对应父节点进行相应调整
- 借兄弟节点删除,删除数据后,父节点调整。在兄弟结点满足关键字最小要求的情况下,兄弟结点需要补充上去一个关键字充当父亲结点;
- 借不了兄弟结点,删除数据后,父节点调整。需要继续合并子节点。
哈希表
给定一个长度为10,标号为**[0..9]的存储表
给定一组关键字,你需要把这组数据以规定的方法放进存储表中
首先把关键字的后四位数字求和**,该和对10求模,然后按照求模结果,放进存储表中对应标号的位置。
(例如,求模结果是2,则这个关键字应该放在存储表中标号为2的位置)但是,不同的关键字可能会产生相同的求模结果。
Hash表-线性探测法解决冲突
那么你需要在存储表中为较晚输入的关键字探测到一个空闲位置,该探测方法为标号+1、-1、+2、-2、+3、-3…
例如当前求模结果依然是2,但是标号为2的位置已经被占用了,那么首先对该求模结果+1得到3,如果标号为3的位置是空闲,则把该关键字放进标号为3的位置中。如果标号为3的位置依然被占用了或者不存在,则改为-1、+2、-2、+3、-3…以此类推。Hash表-链表法解决冲突
注意在存储的链表表中,把较晚输入的关键字拼接在原来此处关键字的前面,用空格分隔。ASL查找成功的平均查找长度
排序
简单排序
选择排序
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
{
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
int min=i;
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++)
{
if(num[i]>num[j])
{
min=j;
}
}
int tmp=num[min];
num[min]=num[i];
num[i]=tmp;
}
}
插入排序
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
{
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
int key=num[i];//取需要插入的数据作为key值
int j=i-1;
while(num[j]>key&&j>=0)//把比key值小的数据往后覆盖,腾出恰当的位置放置key
{
num[j+1]=num[j];
j=j-1;
}
num[j+1]=key;
}
}
高级排序算法
快速排序
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
using namespace std;
/*最重要的是先去一个mid值作为比较,把整个数组划分为比mid大和比mid小的连块部分*/
int Partition(int s,int t,int*num){
int mid=num[s];
while(s<t)
{
while(s<t)
{
if(num[t]<mid)
{
num[s]=num[t];
break;//容易落下
}
t--;
}
while(s<t)
{
if(num[s]>mid)
{
num[t]=num[s];
break;
}
s++;
}
}
num[s]=mid;
return s;
}
void QuickSort(int s,int t,int*num){
if(s<t){//容易忘截止条件
int pivot=Partition(s,t,num);
QuickSort(s,pivot-1,num);
QuickSort(pivot+1,t,num);
}
}
归并排序
类比有序表合并过程。
堆排序
1 | /*调整*/ |
性能分析
| 时间复杂度 | 瓶颈时间复杂度 | 空间复杂度 | 稳定性 | 要点 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冒泡排序 | O(n2) | O(n2) | O(1) | 稳定 | 交换 |
| 选择排序 | O(n2) | O(n2) | O(1) | 不稳定 | 选择最小值 |
| 插入排序 | O(n2) | O(n2) | O(1) | 稳定 | 线性表的遍历 |
| 快速排序 | O(nlogn) | O(n2) | O(logn) | 不稳定 | 划分 |
| 堆排序 | O(nlogn) | O(nlogn) | O(1) | 不稳定 | 堆化/调整 |
| 归并排序 | O(nlogn) | O(nlogn) | O(n) | 稳定 | 有序表归并 |
思考题
对长度为N的无序序列,如何用不多于3N/2次比较找出最大和最小值?任取一个标准,找到最大值和最小值。
- 先对存储结构相邻两个数据进行比较,这个过程是N/2。
- 再取较小的数据与最小值比较,统共需要比较N/2;取较大的数据与最大值比较,统共需要比较N/2。
中位数问题:用O(n)的平均时间复杂度从无序序列中找出第k大的元素。利用快速排序分治思想
对序列L做划分,设划分位置的下标为i,则在数组中的排序
rank=i-s+1;若rank=k,则找到;
若rank<k,则在L[i+1]~L[n-1]中继续查找
若rank>k,则在L[0]~L[i-1]中继续查找
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
if (s == t) {
return num[s];
}
int pivot = Partition(s, t, num);
int rank = pivot - s + 1;
if (rank == k) {
return num[pivot];
} else if (rank > k) {
return QuickSelect(s, pivot - 1, num, k);
} else {
return QuickSelect(pivot + 1, t, num, k - rank);
}
}
细节
const常量引用
当传参的函数以
const的形式传入时,说明数据不可以修改。只可以拷贝。例如:传递进来的
list参数是一个常量引用,因此不能直接对其进行修改。然而,在函数中直接修改了list中每个元素的值。修改方法是:创建一个新的
List结构体,然后将输入的list复制到新的结构体中,并且在新的结构体上进行修改。在最后将修改后的List结构体返回,而不是修改输入的list结构体本身。
while(cur)
在某些情况下,两者的使用会产生不同的效果。对于一些编译器而言,
NULL可能被定义为0,因此while(!cur)可能被视为while(cur == 0),而这在语义上并不是一样的。因此,建议使用while(cur != NULL)来明确表达代码意图,代码更加清晰易懂。
memset
函数可以用来将一块内存区域的值全部设置为特定的值。通常情况下,我们可以使用memset将数组的所有元素初始化为0。以下是一个使用memset函数将数组初始化为0的示例代码:
2
memset(arr, 0, sizeof(arr));